Discover how FDA’s rare disease hub accelerates drug development with critical support from CDMO services.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has announced an ambitious plan to create a Rare Disease Innovation Hub aimed at fostering the development and commercialization of treatments for rare diseases. This move is set against a backdrop of significant growth in the rare-disease drug market, which has seen double-digit increases in recent years. With this new initiative, the FDA hopes to sustain and potentially accelerate this growth, addressing the unique challenges and opportunities presented by rare diseases.
FDA’s Plan for the Rare Disease Innovation Hub
In July 2024, the FDA revealed its plans to establish the Rare Disease Innovation Hub, designed to leverage cross-agency expertise and enhance inter-center connectivity to drive the development of rare disease treatments. The FDA has long incentivized the creation of orphan drugs—prescription medicines for rare diseases affecting fewer than 200,000 people in the US—through market-exclusivity and regulatory-review measures. The new Hub aims to further bolster these efforts.
“Recent rapid advances in the identification of promising drug targets and development of gene therapies offer momentum and potential to meet the needs of patients with rare diseases,” said Patrizia Cavazzoni, MD, Director of the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), and Peter Marks, MD, PhD, Director of the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER), in a joint statement on July 17, 2024. They highlighted that in 2023, over half of all novel drugs and biologics approved by the FDA were for rare diseases.
The Hub will focus on products intended for smaller populations or diseases with variable and not fully understood natural histories. Its three primary functions include:
1. Serving as a Single Point of Connection: The Hub will engage with the rare-disease community, including patient and caregiver groups, trade organizations, and scientific/academic bodies, to help navigate FDA intersections affecting rare disease patients, such as medical devices and combination products.
2. Enhancing Inter-Center Collaboration: The Hub will address common scientific, clinical, and policy issues related to rare-disease product development, promoting consistency across FDA offices and centers.
3. Advancing Regulatory Science: The Hub will work on novel endpoints, biomarker development, innovative trial designs, real-world evidence, and statistical methods.
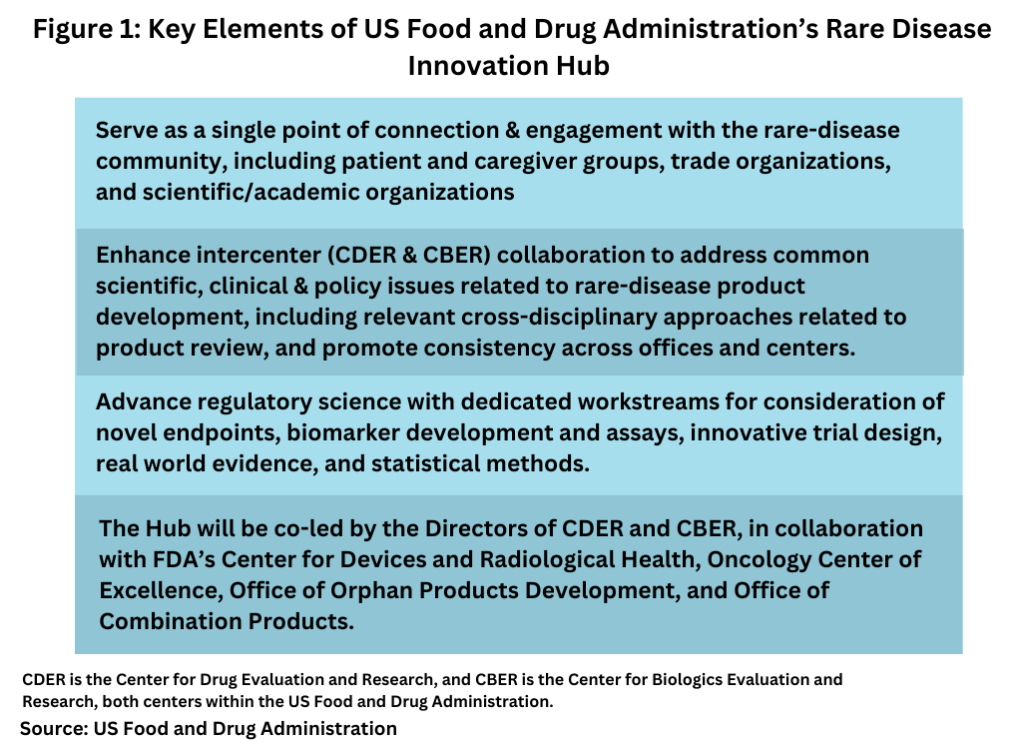
The Hub will be co-led by the Directors of CDER and CBER and will involve collaboration with FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, Oncology Center of Excellence, Office of Orphan Products Development, and Office of Combination Products. A new senior leadership position, Director of Strategic Coalitions for the Hub, will act as the main point of contact for external engagements on rare disease-related issues.
Rare-Disease Drugs Leading Product Innovation
Orphan drugs, despite serving niche patient populations, play a crucial role in the growth strategy and product innovation for both large and small bio/pharmaceutical companies. Over the past five years, orphan drugs have consistently made up more than half of the new molecular entities and therapeutic biologics approved by the FDA’s CDER.
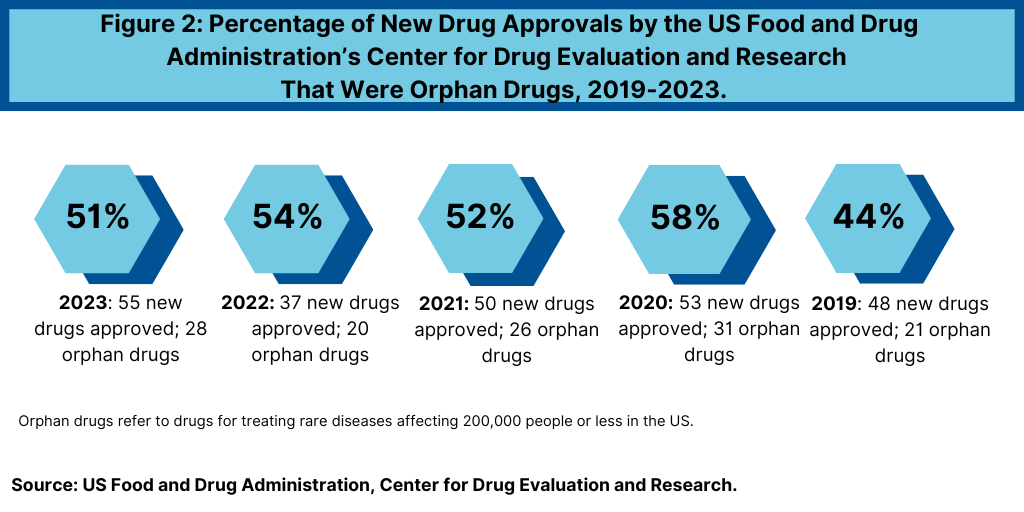
In 2023, orphan drugs constituted 51% of CDER’s novel drug approvals. This trend has been stable, with more than half of the new drug approvals each year from 2019 to 2022 being orphan drugs. This reflects the bio/pharmaceutical industry’s commitment to addressing rare diseases, driven by both market potential and regulatory incentives.
Market Outlook for Orphan Drugs
The orphan drug market has experienced robust growth, outpacing non-orphan prescription drugs with an average annual sales growth of nearly 11% over the past decade. Orphan drugs increased their market share from less than 10% in 2014 to nearly 20% in 2023. Despite projections of a slowdown, orphan drugs are expected to generate $185 billion in revenues in 2024 and reach $270 billion by 2028.
Top orphan drugs are anticipated to maintain their strategic importance, with leading products like Johnson & Johnson’s Darzalex, Vertex Pharmaceuticals’ Trikafta, and Roche’s Hemlibra expected to generate significant revenues.
“Even with the anticipated moderation in growth, orphan drugs continue to punch above their weight class in terms of value,” noted Daniel Chancellor, Director of Thought Leadership at Evaluate. He emphasized that while orphan drugs face mainstream challenges, their development incentives and high-value nature will continue to support this crucial sector.
The establishment of the Rare Disease Innovation Hub by the FDA represents a significant step towards advancing the development and commercialization of rare-disease treatments. By fostering collaboration, enhancing regulatory science, and engaging with the rare-disease community, the FDA aims to sustain the momentum in orphan drug innovation and address the unmet needs of millions of patients. As the market for orphan drugs continues to evolve, the strategic importance of this sector remains undiminished, promising continued growth and innovation in the years to come.
CDMO Services
CDMO Services
Comments are closed.











