Best practice in GMP audits. Learn how these audits ensure compliance with regulatory and maintain high-quality standards in the pharma industry.
Mastering GMP Audits for Compliance and Quality
Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) audits are essential for ensuring compliance and maintaining high-quality standards in the pharmaceutical and biotech industries. These audits help verify that manufacturing processes are consistent, controlled, and meet regulatory requirements.
These audits assess whether a company adheres to Good Manufacturing Practices, which are guidelines set by regulatory bodies like the FDA to ensure the quality, safety, and efficacy of products.
During a GMP audit, auditors review documentation, inspect facilities, and interview staff to verify compliance. The goal is to ensure that products are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards. Regular GMP audits help prevent errors, reduce risks, and maintain consumer trust.
GMP audits typically focus on five key components to assess compliance:
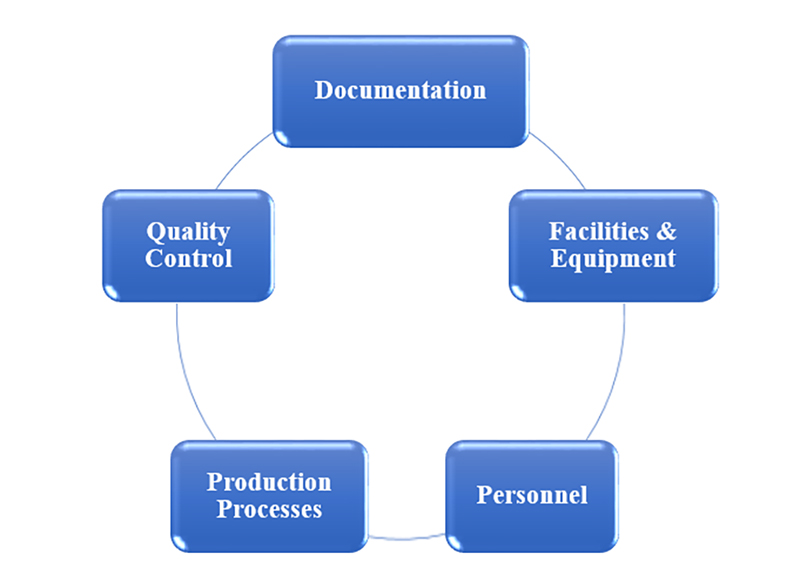
1. Documentation: Accurate and thorough records are essential. This includes batch records, SOPs, training logs, and maintenance records.
2. Facilities and Equipment: The physical state of the manufacturing environment and equipment maintenance are scrutinized to ensure they meet GMP standards.
3. Personnel: Auditors evaluate staff training and qualifications to ensure they are competent to perform their roles.
4. Production Processes: The consistency and control of manufacturing processes are examined to ensure they produce high-quality products.
5. Quality Control: Auditors assess quality control procedures, including testing and release processes, to ensure products meet specifications.
Ensuring these components are in place and functioning effectively is crucial for a successful GMP audit.
The 5 Ps of GMP audits are key areas that auditors focus on during their evaluation:
Focusing on these areas helps organizations prepare for GMP audits and maintain compliance.
Implementing the best practices for handling GMP audits can make a significant difference in the audit outcome, ensuring your facility remains compliant and efficient. In this blog, we will explore ten best practices for handling GMP audits.

1. Prepare Thoroughly for GMP Audits
Preparation is crucial for a successful GMP audit. Ensure all documentation is up-to-date and easily accessible. Conduct internal audits regularly to identify and address potential issues before the official audit. Train staff on GMP principles and audit procedures, emphasizing the importance of accurate record-keeping and adherence to protocols.
Thorough preparation includes reviewing past audit reports, understanding common audit findings, and implementing corrective actions. Regular internal audits can help identify gaps and areas for improvement, ensuring your facility is always ready for an external GMP audit.
2. Maintain Comprehensive Documentation
Accurate and comprehensive documentation is the backbone of GMP compliance. Ensure all records, including batch records, standard operating procedures (SOPs), and training records, are complete, accurate, and up-to-date. Proper documentation demonstrates your commitment to quality and compliance during GMP audits.
Invest in a robust document management system to streamline documentation processes. Ensure that all staff are trained on the importance of meticulous record-keeping and understand how to properly document their activities. Regularly review and update documents to reflect current practices and regulatory requirements.
3. Foster a Culture of Quality and Compliance
Creating a culture that prioritizes quality and compliance is essential for successful GMP audits. Encourage open communication and continuous improvement among staff. Implement regular training programs to keep employees informed about GMP standards and updates. Recognize and reward compliance efforts to motivate staff.
A strong quality culture ensures that GMP principles are integrated into daily operations. Encourage employees to take ownership of their roles in maintaining compliance and quality. Regularly review performance metrics and feedback to identify areas for improvement and implement corrective actions promptly.
4. Conduct Mock Audits and Gap Assessments
Mock audits and gap assessments are valuable tools for identifying weaknesses in your GMP compliance program. Conduct regular mock audits to simulate the official audit process and identify potential issues. Use the findings to implement corrective actions and improve your readiness for actual GMP audits.
Gap assessments help identify areas where your processes may fall short of regulatory requirements. Addressing these gaps proactively can prevent non-compliance issues during official audits. Regular mock audits also help staff become familiar with the audit process, reducing anxiety and improving performance during actual audits.
5. Engage with Experienced Auditors
Engaging with experienced auditors can provide valuable insights and guidance for improving GMP compliance. External consultants can offer an objective perspective and identify areas for improvement that internal staff may overlook. Consider bringing in experts for periodic reviews and training sessions.
Experienced auditors can help you navigate complex regulatory requirements and ensure your facility is meeting the highest standards of quality and compliance. Their expertise can also help you develop more effective audit strategies and improve your overall GMP program.

6. Implement Robust Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA)
Corrective and preventive actions (CAPA) are critical for addressing non-compliance issues and preventing recurrence. Develop a robust CAPA program to identify root causes, implement corrective actions, and monitor their effectiveness. Document all CAPA activities thoroughly to demonstrate compliance during GMP audits.
Ensure that CAPA processes are integrated into your quality management system and that staff are trained on how to implement them effectively. Regularly review CAPA reports to identify trends and take proactive measures to address underlying issues. A strong CAPA program is essential for continuous improvement and maintaining GMP compliance.
7. Stay Updated with Regulatory Changes
Regulatory requirements for GMP compliance are constantly evolving. Stay informed about changes to regulations and guidelines to ensure your facility remains compliant. Subscribe to industry newsletters, attend conferences, and participate in professional organizations to stay current with the latest developments in GMP regulations.
Regularly review and update your SOPs and quality management system to reflect changes in regulatory requirements. Ensure that staff are informed about updates and trained on new procedures. Staying proactive about regulatory changes can help you avoid non-compliance issues and ensure successful GMP audits.
8. Foster Strong Supplier Relationships
Your suppliers play a crucial role in maintaining GMP compliance. Develop strong relationships with your suppliers to ensure they adhere to GMP standards. Conduct regular audits of your suppliers to verify their compliance and address any issues promptly.
Collaborate with suppliers to ensure they understand your quality requirements and are committed to meeting them. Establish clear communication channels and provide regular feedback to help suppliers improve their processes. A strong partnership with compliant suppliers can significantly enhance your GMP compliance program.
9. Leverage Technology for GMP Compliance
Technology can streamline many aspects of GMP compliance, from documentation management to process monitoring. Invest in quality management software to automate documentation, track deviations, and manage CAPA activities. Use electronic systems to monitor environmental conditions and ensure consistent production processes.
Implementing technology can improve efficiency, reduce the risk of human error, and provide real-time insights into your GMP compliance status. Ensure that all technology systems are validated and comply with regulatory requirements. Regularly review and update your technology solutions to keep pace with advancements and maintain compliance.
10. Review and Improve Continuously
Continuous improvement is essential for maintaining GMP compliance. Regularly review your GMP program to identify areas for improvement and implement changes as needed. Use audit findings, CAPA reports, and performance metrics to drive continuous improvement efforts.
Encourage a mindset of continuous improvement among staff and provide training on quality improvement methodologies. Regularly assess the effectiveness of your GMP program and make necessary adjustments to ensure it remains effective and compliant. A commitment to continuous improvement can help you stay ahead of regulatory changes and maintain a high level of quality and compliance.
GMP and Current Good Manufacturing Practices (CGMP) are terms often used interchangeably, but there are differences:
- GMP: Refers to general guidelines for manufacturing processes to ensure product quality and safety.
- CGMP: Emphasizes the “current” aspect, highlighting the need to stay up-to-date with the latest regulations and technological advancements. Adhering to CGMP ensures that manufacturing practices evolve with industry standards, maintaining high levels of quality and compliance.
This blog post aims to provide valuable insights into handling GMP audits effectively. By following these best practices, you can ensure your facility remains compliant and maintains high-quality standards. Implementing these strategies will help you navigate the complexities of GMP audits and achieve successful outcomes.
GMP Audits
GMP Audits
Comments are closed.